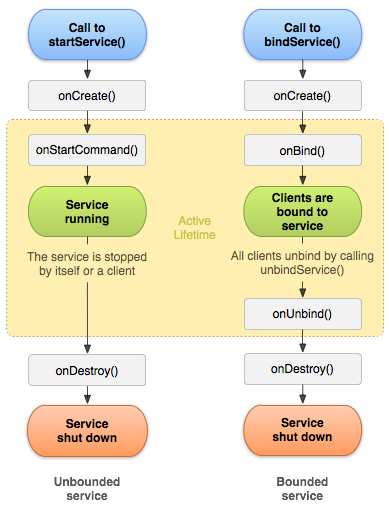
bound Service(绑定服务)是 client-server 模式中的 server。它允许组件绑定到服务,发送请求,接收饭后结果并执行 IPC。 绑定服务只有当它服务于别的组件的时候才会存活,并且不会一直在后台运行。
Note: 如果你的 app 是 5.0(API level 21) 以上,推荐你使用 JobScheduler来执行后台 services。
创建绑定服务
我们需要提供一个 IBinder 来提供接口来让客户端与服务进行通讯,我们可以通过下面3种方式来定义接口:
- 继承 Binder 类
如果服务不需要跨进程调用,那么就要继承 Binder 类来创建通信接口并且将之在 onBind() 中返回。客户端可以获得这个 Binder 来调用 Binder 或者 Service 中的接口。public class LocalService extends Service { // Binder given to clients private final IBinder mBinder = new LocalBinder(); // Random number generator private final Random mGenerator = new Random(); /** * Class used for the client Binder. Because we know this service always * runs in the same process as its clients, we don't need to deal with IPC. */ public class LocalBinder extends Binder { LocalService getService() { // Return this instance of LocalService so clients can call public methods return LocalService.this; } } @Override public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) { //在 onBind 中将 IBinder 返回给客户端 return mBinder; } /** method for clients */ public int getRandomNumber() { return mGenerator.nextInt(100); } }创建一个 LocalBinder,然后再 onBind() 中返回给客户端,那么客户端就可以调用 LocalBinder 中的方法,如 getService 获得 Service 的实例,那么就可以调用 Service 里面的方法,如 getrandomNumber()了。
public class BindingActivity extends Activity { LocalService mService; boolean mBound = false; @Override protected void onStart() { super.onStart(); // Bind to LocalService Intent intent = new Intent(this, LocalService.class); bindService(intent, mConnection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE); } @Override protected void onStop() { super.onStop(); unbindService(mConnection); mBound = false; } /** Called when a button is clicked (the button in the layout file attaches to * this method with the android:onClick attribute) */ public void onButtonClick(View v) { if (mBound) { // Call a method from the LocalService. // However, if this call were something that might hang, then this request should // occur in a separate thread to avoid slowing down the activity performance. int num = mService.getRandomNumber(); } } /** Defines callbacks for service binding, passed to bindService() */ private ServiceConnection mConnection = new ServiceConnection() { @Override public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName className, IBinder service) { // We've bound to LocalService, cast the IBinder and get LocalService instance LocalBinder binder = (LocalBinder) service; mService = binder.getService(); mBound = true; } @Override public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName arg0) { mBound = false; } }; }Service 创建好后,我们就可以在组件中使用了,首先创建一个 ServiceConnection ,在 onServiceConnected 中接收 Service 中 onBind() 返回的 IBinder,然后通过 bindService 来绑定。
- 使用 Messenger
如果你需要接口支持跨进程,你可以使用 Messenger。public class MessengerService extends Service { /** Command to the service to display a message */ static final int MSG_SAY_HELLO = 1; /** * Handler of incoming messages from clients. */ class IncomingHandler extends Handler { @Override public void handleMessage(Message msg) { switch (msg.what) { case MSG_SAY_HELLO: Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "hello!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); break; default: super.handleMessage(msg); } } } /** * Target we publish for clients to send messages to IncomingHandler. */ final Messenger mMessenger = new Messenger(new IncomingHandler()); /** * When binding to the service, we return an interface to our messenger * for sending messages to the service. */ @Override public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) { return mMessenger.getBinder(); } }我们创建一个 Handler,然后传给 Messenger,再在 onBind 中将 Messenger 的 binder 返回即可。
public class ActivityMessenger extends Activity { /** Messenger for communicating with the service. */ Messenger mService = null; /** Flag indicating whether we have called bind on the service. */ boolean mBound; /** * Class for interacting with the main interface of the service. */ private ServiceConnection mConnection = new ServiceConnection() { public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName className, IBinder service) { // This is called when the connection with the service has been // established, giving us the object we can use to // interact with the service. We are communicating with the // service using a Messenger, so here we get a client-side // representation of that from the raw IBinder object. mService = new Messenger(service); mBound = true; } public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName className) { // This is called when the connection with the service has been // unexpectedly disconnected -- that is, its process crashed. mService = null; mBound = false; } }; public void sayHello(View v) { if (!mBound) return; // Create and send a message to the service, using a supported 'what' value Message msg = Message.obtain(null, MessengerService.MSG_SAY_HELLO, 0, 0); try { mService.send(msg); } catch (RemoteException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @Override protected void onStart() { super.onStart(); // Bind to the service bindService(new Intent(this, MessengerService.class), mConnection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE); } @Override protected void onStop() { super.onStop(); // Unbind from the service if (mBound) { unbindService(mConnection); mBound = false; } } }跟前面不一样的就是在 onServiceConnected 后,会使用里面的 IBinder 创建一个 Messenger 然后通过它来发送 Message 来实现通讯。
这是执行进程间通信的最简单的方式,因为 Messenger 将所有的请求都放到单线程的队列中,这样就不用设计 Service 支持多线程了。 - 使用 AIDL
前面的 Messenger 实际上是基于 AIDL 实现的,但 Messenger 会创建一个队列,所有的客户端请求都在一个单线程中执行。如果你希望你的服务能同时处理多个任务,你就需要直接使用 AIDL。那么你的服务必须是线程安全的。
大部分的应用都不应该使用 AIDL, 因为它需要服务支持多线程,这样就会造成复杂的实现。