作用
当 activity 变得容易销毁的时候,activity、activity 内的 View 和 Fragment 会调用 onSaveInstanceState 方法来存储数据。如果 Activity 销毁了,则会使用 onRestoreInstanceState 来恢复数据(onSaveInstanceState 中保存的数据在恢复时也会传给 onCreate)。
调用场景
onSaveInstanceState
- 按下 Home 键,Activity 进入后台时
- 按下电源键,屏幕关闭,Activity 进入后台
- 启动其他 Activity
- 横竖屏切换
如果是用户点击 back,或者主动调用 finish 方法来关闭 Activity,而不是 Activity 进入后台后被杀掉的话,是不会调用的。
onRestoreInstanceState
在 Activity 被系统销毁后,恢复 Activity 时会调用。
可以看出 onSaveInstanceState 方法 和 onRestoreInstanceState 方法并不是成对出现的。
调用时机
onSaveInstanceState 出现在 onStop 或 onPause 之前,onRestoreInstanceState 出现在 onstart 与 onResume 之间。
下面是旋转屏幕时,Activity 的生命周期的变化图:
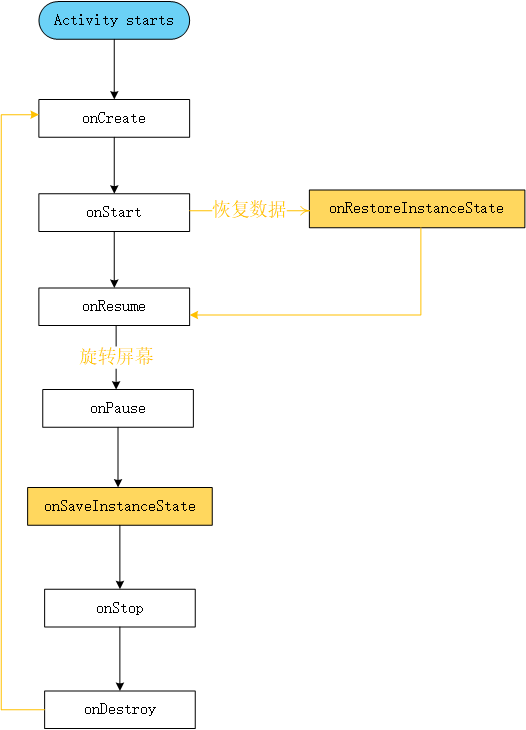 注意,onSaveInstanceState 并不一定在 onPause 之后调用。
注意,onSaveInstanceState 并不一定在 onPause 之后调用。
onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) 中既然能恢复数据,为什么还需要 onRestoreInstanceState?
如果是在 onCreate 中进行恢复数据的话,会导致每次创建(而非恢复)Activity 的时候也要有处理这个 bundle (判断是否为空)的逻辑。而且用 onRestoreInstanceState 方法,我们可以将恢复的逻辑和创建的逻辑解耦。
什么时候用到 onSaveInstanceState?
由于 View 中都有默认的 onSaveInstanceState 方法,只要这个 View 有 id,当 Activity 被系统杀死时,它会自动保存 UI 的一些状态。譬如往 EditText 中输入数据后,切换横屏,这时候数据是自动被保存的,不需要我们去重写 onSaveInstanceState 进行处理。所以一般情况下,我们是不需要重写的。
源码解析
默认的 onSaveInstanceState 保存了些什么
protected void onSaveInstanceState(Bundle outState) {
outState.putBundle(WINDOW_HIERARCHY_TAG, mWindow.saveHierarchyState());
outState.putInt(LAST_AUTOFILL_ID, mLastAutofillId);
Parcelable p = mFragments.saveAllState();
if (p != null) {
outState.putParcelable(FRAGMENTS_TAG, p);
}
if (mAutoFillResetNeeded) {
outState.putBoolean(AUTOFILL_RESET_NEEDED, true);
getAutofillManager().onSaveInstanceState(outState);
}
getApplication().dispatchActivitySaveInstanceState(this, outState);
}
可以看到它调用了 mWindow.saveHierarchyState 来遍历 Activity 的 view 树,然后调用 mFragments.saveAllState 来保存 Fragment 的数据。
- 首先我们来看看 window.saveHierarchyState:
window 是一个抽象类,实现类是 PhoneWindow,我们来看看它的 saveHierarchyState:public Bundle saveHierarchyState() { Bundle outState = new Bundle(); if (mContentParent == null) { return outState; } SparseArray<Parcelable> states = new SparseArray<Parcelable>(); //保存 Activity 中的 View 的状态 mContentParent.saveHierarchyState(states); outState.putSparseParcelableArray(VIEWS_TAG, states); // Save the focused view ID. final View focusedView = mContentParent.findFocus(); if (focusedView != null && focusedView.getId() != View.NO_ID) { outState.putInt(FOCUSED_ID_TAG, focusedView.getId()); } // save the panels SparseArray<Parcelable> panelStates = new SparseArray<Parcelable>(); savePanelState(panelStates); if (panelStates.size() > 0) { outState.putSparseParcelableArray(PANELS_TAG, panelStates); } if (mDecorContentParent != null) { SparseArray<Parcelable> actionBarStates = new SparseArray<Parcelable>(); mDecorContentParent.saveToolbarHierarchyState(actionBarStates); outState.putSparseParcelableArray(ACTION_BAR_TAG, actionBarStates); } return outState; }它调用了 mContentParent.saveHierarchyState(states),mContentParent 是 DecorView 或者 DecorView 的 child。由于它是一个 ViewGroup,没有 saveHierarchyState 方法,这里它掉的是 View 的方法:
public void saveHierarchyState(SparseArray<Parcelable> container) { dispatchSaveInstanceState(container); }再来看看 ViewGroup 和 View 的 dispatchSaveInstanceState 方法:
protected void dispatchSaveInstanceState(SparseArray<Parcelable> container) { //ViewGroup 会调用 View 的 dispatchSaveInstanceState 来保存自己的状态 super.dispatchSaveInstanceState(container); final int count = mChildrenCount; final View[] children = mChildren; //遍历子 View 调用子 View 的方法来保存状态 for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { View c = children[i]; if ((c.mViewFlags & PARENT_SAVE_DISABLED_MASK) != PARENT_SAVE_DISABLED) { c.dispatchSaveInstanceState(container); } } } protected void dispatchSaveInstanceState(SparseArray<Parcelable> container) { if (mID != NO_ID && (mViewFlags & SAVE_DISABLED_MASK) == 0) { mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_SAVE_STATE_CALLED; //获得子 View 的状态 Parcelable state = onSaveInstanceState(); if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_SAVE_STATE_CALLED) == 0) { throw new IllegalStateException( "Derived class did not call super.onSaveInstanceState()"); } if (state != null) { //将子 View 的状态保存到 Activity 的 SparseArray 中。注意,它的 key 为 View 的 id。 //如果 View 没有设置 id 的话,状态是不会被保存的 container.put(mID, state); } } } - 再来看看如何保存 Fragment 的状态的:
它最终是调用到 FragmentMangerImpl 的 SaveAllState 方法:Parcelable saveAllState() { ... // First collect all active fragments. int N = mActive.size(); FragmentState[] active = new FragmentState[N]; boolean haveFragments = false; //遍历 Fragment 并给每一个 Fragment 创建一个 FragmentState 保存状态 for (int i=0; i<N; i++) { Fragment f = mActive.valueAt(i); if (f != null) { ... if (f.mState > Fragment.INITIALIZING && fs.mSavedFragmentState == null) { //保存 Fragment 基本状态 fs.mSavedFragmentState = saveFragmentBasicState(f); if (f.mTarget != null) { if (fs.mSavedFragmentState == null) { fs.mSavedFragmentState = new Bundle(); } putFragment(fs.mSavedFragmentState, FragmentManagerImpl.TARGET_STATE_TAG, f.mTarget); if (f.mTargetRequestCode != 0) { fs.mSavedFragmentState.putInt( FragmentManagerImpl.TARGET_REQUEST_CODE_STATE_TAG, f.mTargetRequestCode); } } } else { fs.mSavedFragmentState = f.mSavedFragmentState; } } } int[] added = null; BackStackState[] backStack = null; // Build list of currently added fragments. N = mAdded.size(); if (N > 0) { added = new int[N]; for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { added[i] = mAdded.get(i).mIndex; } } // Now save back stack. if (mBackStack != null) { N = mBackStack.size(); if (N > 0) { backStack = new BackStackState[N]; for (int i=0; i<N; i++) { backStack[i] = new BackStackState(mBackStack.get(i)); } } } FragmentManagerState fms = new FragmentManagerState(); fms.mActive = active; fms.mAdded = added; fms.mBackStack = backStack; if (mPrimaryNav != null) { fms.mPrimaryNavActiveIndex = mPrimaryNav.mIndex; } fms.mNextFragmentIndex = mNextFragmentIndex; saveNonConfig(); return fms; }我们看看 saveFragmentBasicState 中保存了哪些基本状态:
Bundle saveFragmentBasicState(Fragment f) { Bundle result = null; if (mStateBundle == null) { mStateBundle = new Bundle(); } //调用 Fragment 的 onSaveInstanceState 方法,并调用子 Fragment 的 saveAllState 方法 f.performSaveInstanceState(mStateBundle); dispatchOnFragmentSaveInstanceState(f, mStateBundle, false); if (!mStateBundle.isEmpty()) { result = mStateBundle; mStateBundle = null; } if (f.mView != null) { //保存 Fragment 的 View 数据,最终调用到 View 的 saveHierarchyState,和前面保存 Activity 的 View 一样。 saveFragmentViewState(f); } if (f.mSavedViewState != null) { if (result == null) { result = new Bundle(); } //将上面保存的 View 的数据保存到 Bundle 中 result.putSparseParcelableArray( FragmentManagerImpl.VIEW_STATE_TAG, f.mSavedViewState); } if (!f.mUserVisibleHint) { if (result == null) { result = new Bundle(); } // Only add this if it's not the default value result.putBoolean(FragmentManagerImpl.USER_VISIBLE_HINT_TAG, f.mUserVisibleHint); } return result; }我们可以看出,saveAllState() 方法会像 Activity 那样,保存 Fragment 中 View 数的状态。
onSaveInstanceState 是如何被调用的?
- 我们首先来看看 Activity 在 pause 的时候会不会调用 onSaveInstanceState 方法:
final Bundle performPauseActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, boolean finished, boolean saveState, String reason) { if (r.paused) { if (r.activity.mFinished) { // If we are finishing, we won't call onResume() in certain cases. // So here we likewise don't want to call onPause() if the activity // isn't resumed. return null; } RuntimeException e = new RuntimeException( "Performing pause of activity that is not resumed: " + r.intent.getComponent().toShortString()); Slog.e(TAG, e.getMessage(), e); } if (finished) { r.activity.mFinished = true; } // Next have the activity save its current state and managed dialogs... if (!r.activity.mFinished && saveState) { callCallActivityOnSaveInstanceState(r); } performPauseActivityIfNeeded(r, reason); // Notify any outstanding on paused listeners ArrayList<OnActivityPausedListener> listeners; synchronized (mOnPauseListeners) { listeners = mOnPauseListeners.remove(r.activity); } int size = (listeners != null ? listeners.size() : 0); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { listeners.get(i).onPaused(r.activity); } return !r.activity.mFinished && saveState ? r.state : null; }在 PerformPauseActivity 的时候,会调用 callCallActivityOnSaveInstanceState()。但是有一个条件
r.activity.mFinished && saveState。mFinished 值只有当调用了 finish() 方法才会为 true。而这里刚调用 onPause 方法,所以 mFinished 为 false。那么只有 saveState 返回 true 才会执行该方法。 saveState 是由下面这个函数来决定的:public boolean isPreHoneycomb() { if (activity != null) { return activity.getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion < android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.HONEYCOMB; } return false; }只要 targetSdk < 11 就返回 true。那么意思就是只要没有调用 finish() 方法,则不会调用 callCallActivityOnSaveInstanceState 方法。
private void callCallActivityOnSaveInstanceState(ActivityClientRecord r) { r.state = new Bundle(); r.state.setAllowFds(false); if (r.isPersistable()) { r.persistentState = new PersistableBundle(); mInstrumentation.callActivityOnSaveInstanceState(r.activity, r.state, r.persistentState); } else { mInstrumentation.callActivityOnSaveInstanceState(r.activity, r.state); } }Instrumentation 里的该函数:
public void callActivityOnSaveInstanceState(Activity activity, Bundle outState, PersistableBundle outPersistentState) { activity.performSaveInstanceState(outState, outPersistentState); }再看看 activity 的 performSaveInstanceState:
final void performSaveInstanceState(Bundle outState) { onSaveInstanceState(outState); saveManagedDialogs(outState); mActivityTransitionState.saveState(outState); }总结:只有在 andriod 3.0 之前并且没有调用 finish() 才会在 onPause 之前执行 onSavedInstanceState 方法。
- 下面来看看 Activity 在 stop 的时候会不会调用 onSaveInstanceState 方法:
在 Activity 执行 onStop 时会调用到 ActivityThread 中的 handleStopActivity() 方法,最终会调用到:private void performStopActivityInner(ActivityClientRecord r, StopInfo info, boolean keepShown, boolean saveState, String reason) { if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, "Performing stop of " + r); if (r != null) { if (!keepShown && r.stopped) { if (r.activity.mFinished) { // If we are finishing, we won't call onResume() in certain // cases. So here we likewise don't want to call onStop() // if the activity isn't resumed. return; } RuntimeException e = new RuntimeException( "Performing stop of activity that is already stopped: " + r.intent.getComponent().toShortString()); } // One must first be paused before stopped... performPauseActivityIfNeeded(r, reason); // Next have the activity save its current state and managed dialogs... if (!r.activity.mFinished && saveState) { if (r.state == null) { callCallActivityOnSaveInstanceState(r); } } } }可以看出和 pause 一样,这个函数的调用取决于 mFinisheded 和 saveState 决定,不同的是:
private void handleStopActivity(IBinder token, boolean show, int configChanges, int seq) { ... StopInfo info = new StopInfo(); performStopActivityInner(r, info, show, true, "handleStopActivity"); ... }在 handleStopActivity 里 saveState 直接为 true,那么就会执行。
- 下面再来看看为什么点击返回是不会执行 onSaveInstanceState 方法:
public void finishAfterTransition() { if (!mActivityTransitionState.startExitBackTransition(this)) { finish(); } }点击 back 键会触发 onBackPressed 最终会调用到 finish() 方法,将 mFinished 设置为 true,所以这种间接调用 finish() 方法也是不会调用 onSaveInstanceState 方法的。