内存泄漏示例
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private lateinit var ctx: Context
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
ctx = this
LeakThread().start()
}
inner class LeakThread : Thread() {
override fun run() {
super.run()
Thread.sleep(5000 * 20)
}
}
}
获取内存泄漏文件
打开应用后,一直返回关掉所有的 activity 回到桌面,然后通过执行 adb shell dumpsys meminfo [package name] 得到该进程的相关信息。
譬如: 执行 adb shell dumpsys meminfo com.example.leak 得到如下数据:
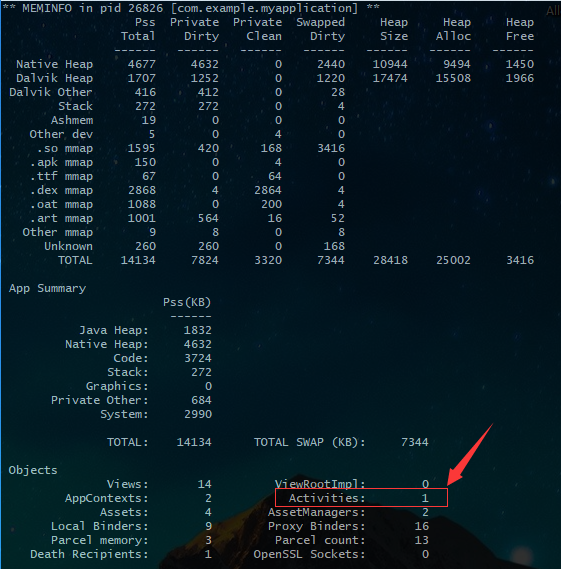
可以看到有一个 activity 泄漏了。然后我们通过 adb shell am dumpheap com.example.leak /sdcard/leak.hprof 将数据写到 sdcard 中的 leak.hprof 文件中,然后 pull 到电脑上。
使用 MAT 分析内存泄漏
使用 MAT 导入生成的 hprof 文件后,会看到一个饼状图,该图展示当前占用内存最多的对象,我们接下来点击上面的 histogram ,它直接展示当前内存中各种类型对象的数量、shallow heap(某个对象占用的内存的大小) 和 retained heap(该对象的 shallow heap 和该对象能直接或间接访问到的对象的 shallow heap 之和)。
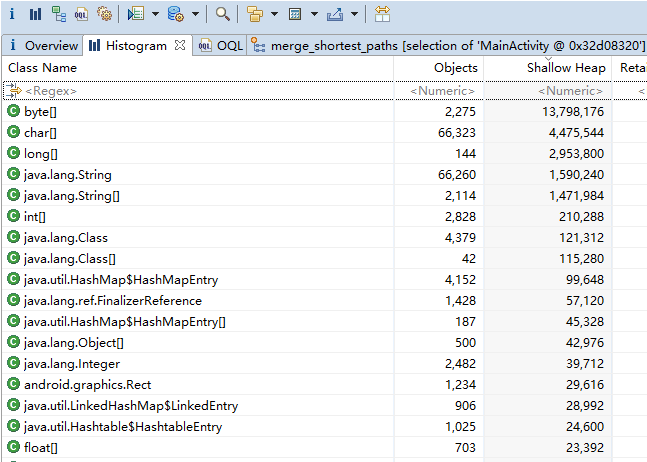
下面我们来看看哪些 Activity 泄漏了:
我们点击上面的 OQL(Object Query Language) 这时就会出现一个让你输入 “sql” 语句的面板。
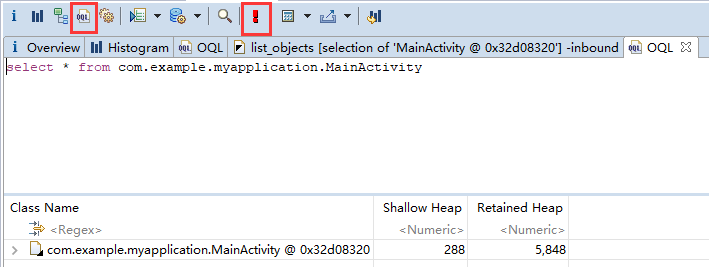
输入 select * from instanceof android.app.Activity 然后按 F5 (或者工具栏上红色的感叹号)来查询当前内存中的所有 Activity 。
如果想单独查询某个类,可以用 select * from [类的完整路径] 即可,如 select * from com.example.myapplication.MainActivity。
右键点击泄漏的类,选中 Merge Shortest Paths to GC Roots,然后点击 exclude all phantom/weak/soft etc. references (将可以被 GC 回收的对象排除掉)来查看一个对象到 GC Roots 的引用链。Java 是通过可达性(Reachability Analysis)来判断对象是否存活,它通过一系列被称为 “GC Roots” 的对象作为起始点,从这些节点向下搜索,搜索所走的路径被称为引用链。如果该对象到 Gc Roots 没有引用链相连,那么该对象则是可回收对象,否则就不能被回收。
除了使用 merge Shortest Paths to GC Roots 外,我们还可以右键选中泄漏的 Activity 选择 List objects 会出现 with incoming reference (内部引用) 和 with outcoming reference (外部引用)。 然后点击 with incoming reference 看该 Activity 的引用路径。然后右键点击该类,选择 Path To Gc Roots -> exclude all phantom/weak/soft etc. references 即可。
我们可以看到是 LeakThread 持有了 MainActivity 的引用造成内存泄漏的。